Your Organs of locomotion in animals images are available in this site. Organs of locomotion in animals are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Organs of locomotion in animals files here. Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for organs of locomotion in animals images information connected with to the organs of locomotion in animals topic, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our website always gives you suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Organs Of Locomotion In Animals. These animals secrete a film of mucus, then creep through it on numerous cilia. Primarily aquatic mammals such as seals, etc., have much more ungainly gaits. Movement is the change in position of only a part of the body. Which is the organ of locomotion?
 Movement in Animals Class 6 Science lesson NCERT CBSE From youtube.com
Movement in Animals Class 6 Science lesson NCERT CBSE From youtube.com
Ciliary locomotion can be quite fast: We have found 1 answer (s) for the clue „organ of locomotion and balance in fishes and some other aquatic animals“. Most of the animals have bilateral symmetry and hence their organs are arranged in symmetric way on both the sides. The circular muscles are radially placed in the body. 14.5 support and movement in animals. It is slow creeping type of locomotion which is performed with the help of.
The locomotion is brought about by the simultaneous action of cilia of all the cells of the colony.
As viewed from evolutionary taxonomy, there are three basic forms of animal locomotion in the terrestrial environment: As viewed from evolutionary taxonomy, there are three basic forms of animal locomotion in the terrestrial environment: Cilia are also responsible for locomotion in some much larger organisms, such as flatworms (platyhelminthes). Movement is the change in position of only a part of the body. In different annelidan species, locomotion is not caused by any individual locomotory agent, but it is the resultant outcome of a coordinated effort of all those three agencies. Try to find some letters, so you can find your solution more easily.
 Source: biology4isc.weebly.com
Source: biology4isc.weebly.com
As viewed from evolutionary taxonomy, there are three basic forms of animal locomotion in the terrestrial environment: Up to 10,000 body lengths per hour for paramecium. Animals must use a single muscular contraction to lift the entire mass off the ground. The anatomical structures that animals use for movement, including cilia, legs, wings, arms, fins, or tails are sometimes referred to as locomotory organs or locomotory structures. Unicellular animals swim by cilia or flagella, crawl about with pseudopodia, make withdrawal movements on a stalk that coils up like a stretched spring, or glide along without apparent deformation in shape.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Learn all the concepts on motility This movement involves a wave that runs the length of the body and moves the animal. Ciliary locomotion can be quite fast: Up to 10,000 body lengths per hour for paramecium. Human beings practice an ambulatory bipedal plantigrade type of locomotion.
 Source: pediaa.com
Source: pediaa.com
Organisms of locomotion in invertebrates • the organs of locomotion in the lower animals are varied wings, tube feet, muscular feet and walking legs are some of the locomotry organs found in these animals. Organisms of locomotion in invertebrates • the organs of locomotion in the lower animals are varied wings, tube feet, muscular feet and walking legs are some of the locomotry organs found in these animals. Typical locomotory organs are fins, legs, muscular foot, wings, pseudopodia, etc. Animals must use a single muscular contraction to lift the entire mass off the ground. The locomotion is brought about by the simultaneous action of cilia of all the cells of the colony.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Up to 10,000 body lengths per hour for paramecium. Animals must use a single muscular contraction to lift the entire mass off the ground. Locomotory organs of animals vertebrates and invertebrates zoology 2. Up to 10,000 body lengths per hour for paramecium. Animals of all size and shape move in search of shelter, food, mate and to escape from predators using their different body parts like fins, legs, wings and so on.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
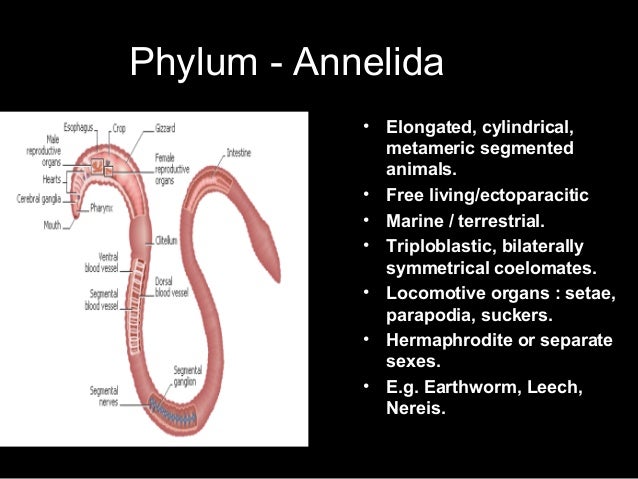
The snake has overcome the handicap of absence of limbs by developing several different methods of locomotion, some of which are seen in other limbless animals, others being unique. The organs of such animals are arranged in a radius of an imaginary circle, e.g. Movement is the change in position of only a part of the body. The first method, called serpentine locomotion, is shared with almost all legless animals, such as some lizards, the caecilians, earthworms, and others. • some invertebrates like roundworms, flatworms, squids, octopus, jellyfish, etc., lack special organs of locomotion.
 Source: amazingfacts4u.com
Source: amazingfacts4u.com
Human beings practice an ambulatory bipedal plantigrade type of locomotion. As viewed from evolutionary taxonomy, there are three basic forms of animal locomotion in the terrestrial environment: This movement involves a wave that runs the length of the body and moves the animal. Unicellular animals swim by cilia or flagella, crawl about with pseudopodia, make withdrawal movements on a stalk that coils up like a stretched spring, or glide along without apparent deformation in shape. If you�ve got another answer, it would be kind of you to add it to our crossword dictionary.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Locomotory organs of animals vertebrates and invertebrates zoology 2. Ciliary locomotion can be quite fast: The locomotory organs vary widely in shape, size and origin. The wrist and ankle bones permit movement in various planes. It is slow creeping type of locomotion which is performed with the help of.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
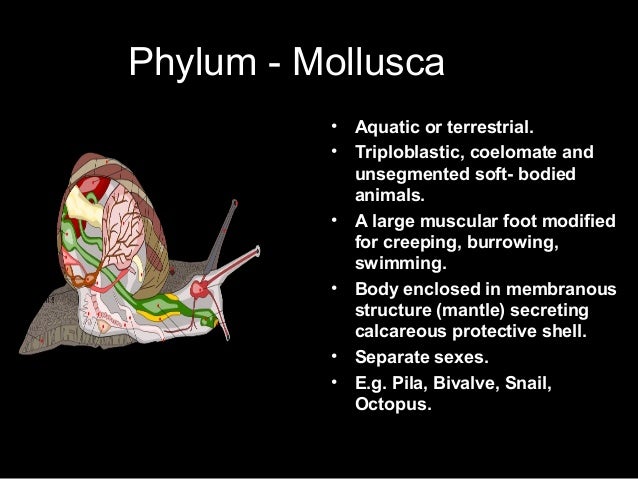
Movement is the change in position of only a part of the body. Locomotary organs in animals 1. Most of the animals have bilateral symmetry and hence their organs are arranged in symmetric way on both the sides. Terrestrial locomotion has evolved as animals adapted from aquatic to terrestrial environments. The organs of such animals are arranged in a radius of an imaginary circle, e.g.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title organs of locomotion in animals by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.